Aptima® Trichomonas vaginalis Assay
Protect and improve the reproductive and sexual health of women through accurate and early detection of symptomatic and asymptomatic Trichomonas vaginalis (TV).
Sense What Can't be Seen
Global prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection is estimated to be higher than for chlamydia and gonorrhoea combined.1 Clinical presentation is an unreliable indicator of TV infection in women, as 10-50% of infections are asymptomatic.2 The Aptima TV assay delivers up to 100% detection in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.3
A Sensitive Assay for Improved Patient Care
The Aptima TV Assay overcomes the challenges of traditional, less sensitive wet mount and culture, making it a highly reliable test to diagnose trichomonas infections.4
Excellent Performance
The Aptima TV assay targets rRNA to deliver up to 100% sensitivity.3
High Sensitivity
Nucleic Acid Amplification tests (NAATs) offer the highest sensitivity for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis.
Sample Stability
Samples collected in Aptima Specimen Collection devices are stable for up to 60 days,3 compared to wet mount preparations which may quickly become negative.5

Simplify & Scale the Future of Diagnostics
The Aptima TV Assay is part of the Hologic Molecular Scalable Solution, a portfolio combining a broad, high-performing assay menu with high-throughput automation. Designed to flexibly scale to meet your needs, from a single patient result to population level screening.
Proven Performance
Detects as little as one organism in the sample. Nearly 50% of TV infections are missed by wet mount.3
Targeting rRNA
for improved assay performance
>95% sensitivity
in specimens from both symptomatic and asymptomatic women
>98% specificity
across clinically relevant sample types
Aligned With UK National Guidelines
"NAATs offer the highest sensitivity for the detection of TV. They should be the test of choice where resources allow and are becoming the current “gold standard.”
UK National Guideline on the Management of TV, 20142

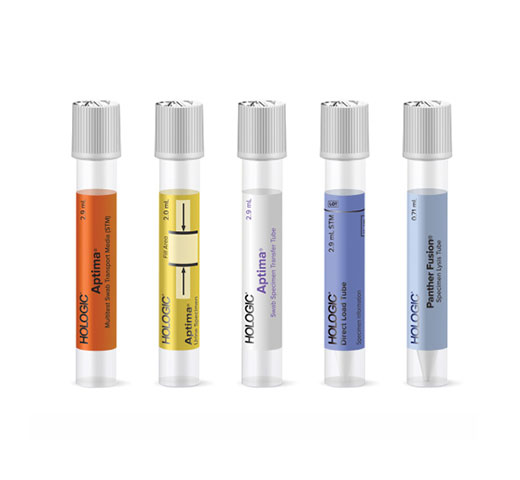
One Sample, Multiple STI Results
Clinically relevant sample type options make the Aptima TV Assay easy to order as a standalone or in combination with other assays from the automated Hologic STI Solution. Browse relevant collection devices below.

Untreated Infections can Cause Serious Consequences3
Trichomonas vaginalis infection has been associated with serious health consequences:
- Adverse pregnancy outcomes including pre-term delivery and low birthweight6,7
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease8
- Prolonged HPV Infection8
- Increased risk of transmition and acquisition of HIV9
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
- Rowly J, Vander Hoon S, Korenromp E, et. al. Chlamydia, gonnorhoea, trichomoniasis and syphilis:global prevalence and incidence estimates 2016. Bull World Health Organ. Aug 2019; 97:548-562
- Sherrard J, Ison C, Moody j. et.al. United Kingdom National Guideline on the Management of Trichomonas vaginalis 2014. Int J STD AIDS 2014;25(8):541-49
- Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis Assay [package insert] AW-23069 Rev.001 San Diego, CA; Hologic, Inc., 2023.
- Nicholls JE, Turner KM, North P, et.al. Cross-sectional study to evaluate trichomonas vaginalis positivity in women tested for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, attending genitourinary medicine and primary care clinics in Bristol, South West England. Sex Transm Infect 2018;94:93-99
- Kingston M, Bansai D, Carlin E. 'Shelf Life' of Trichomonas vaginalis. Int J STD AIDS 2003;14(1):28-29
- Saurina G, McCormack W. Trichomoniasis in pregnancy. Sex Trans Dis 1997;24:361-362.
- Cotch MF, PastoreckJG, Nugent RP, et.al. Trichomonas vaginalis associated with low birth weight and pre-term delivery. Sex Trans Dis 1997; 24: 353-360
- Workowski KA, Bachman LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep 2021;70
- McClelland RS, Sangare L, Hassan WM, et al. Infection with Trichomonas vaginalis increases the risk of HIV-1 acquisition. J Infect Dis. Mar 2007;195:698-702
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Related Products
1434
2797
Hologic BV, Da Vincilaan 5, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium.
Notified Body number wherever applicable